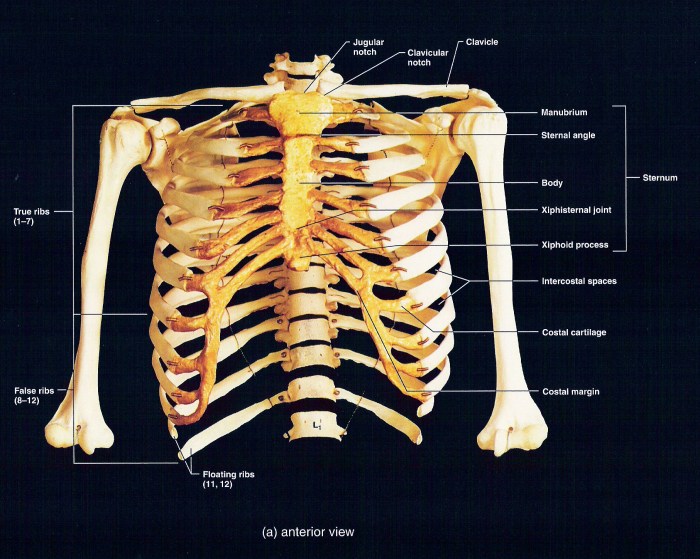
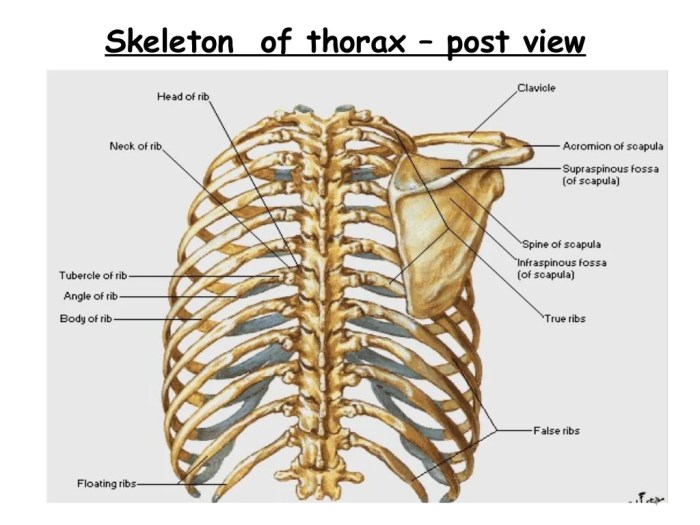
Container for the lungs and heart crossword clue – The container for the lungs and heart, known as the thoracic cavity, is a vital anatomical structure that safeguards and supports these essential organs. Located within the chest, it plays a crucial role in protecting the lungs and heart from external forces and maintaining their optimal function.
This thoracic cavity is a complex structure composed of several anatomical features, including the rib cage, sternum, and diaphragm. Its shape, size, and composition contribute to its protective function, providing a rigid framework and flexible boundaries that cushion and support the delicate organs within.
Container for the Lungs and Heart: Container For The Lungs And Heart Crossword Clue
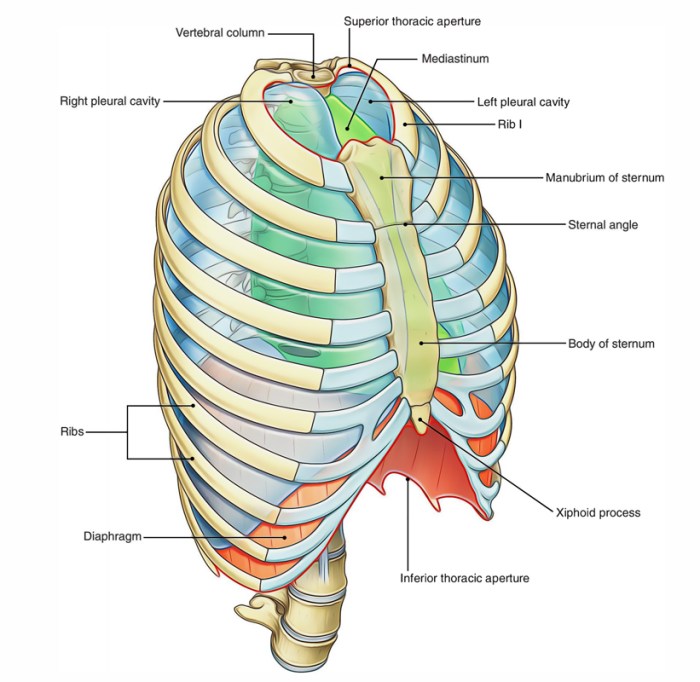
The container for the lungs and heart is a complex structure known as the thoracic cavity. Located in the upper part of the body, the thoracic cavity is enclosed by the rib cage and the diaphragm, which forms its floor.
Its primary function is to protect and support the vital organs it houses, namely the lungs and heart. The thoracic cavity provides a stable and secure environment, shielding these organs from external forces and allowing them to function optimally.
Anatomical Features
The thoracic cavity is a dome-shaped space, with its shape largely determined by the rib cage. The ribs, which form the sides and front of the cavity, are curved and provide a protective framework.
The size of the thoracic cavity varies among individuals, but it generally measures about 30 cm in length, 25 cm in width, and 15 cm in depth. The cavity is lined by a thin membrane called the pleura, which helps to reduce friction and create a smooth surface for the lungs to expand and contract.
Components and Layers, Container for the lungs and heart crossword clue
The thoracic cavity is composed of several key components, each with a specific function:
- Ribs:The 12 pairs of ribs form the bony cage that surrounds the thoracic cavity, providing structural support and protection.
- Sternum:The sternum, or breastbone, is a flat bone located at the front of the thoracic cavity. It connects to the ribs and provides additional support.
- Diaphragm:The diaphragm is a dome-shaped muscle that separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity. It plays a crucial role in breathing by contracting and relaxing to facilitate inhalation and exhalation.
- Pleura:The pleura is a thin membrane that lines the thoracic cavity and covers the lungs. It consists of two layers: the parietal pleura, which lines the cavity walls, and the visceral pleura, which covers the lungs. Between these layers is a fluid-filled space called the pleural cavity, which helps to reduce friction during breathing.
Pathologies and Disorders
The thoracic cavity can be affected by various pathologies and disorders, including:
- Pneumothorax:A condition in which air enters the pleural cavity, causing the lung to collapse.
- Pleural effusion:A buildup of fluid in the pleural cavity, which can cause difficulty breathing and chest pain.
- Lung cancer:Cancer that develops in the lungs, which can lead to a variety of symptoms, including shortness of breath, coughing, and chest pain.
- Heart disease:Conditions that affect the heart, such as coronary artery disease, can impact the function of the thoracic cavity and its ability to protect the heart.
Clinical Significance
The thoracic cavity is of great clinical significance as it houses vital organs and plays a crucial role in respiration. Its assessment and diagnosis are essential in diagnosing and treating various medical conditions.
Imaging techniques, such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs, are commonly used to evaluate the health of the thoracic cavity and its contents. These techniques allow physicians to visualize the lungs, heart, and other structures, helping to identify any abnormalities or disorders.
Essential FAQs
What is the primary function of the container for the lungs and heart?
The primary function of the container for the lungs and heart is to provide protection and support to these vital organs, ensuring their optimal functioning.
What are the common pathologies and disorders that can affect the container for the lungs and heart?
Common pathologies and disorders that can affect the container for the lungs and heart include conditions such as chest trauma, rib fractures, and pericarditis, which can impact its protective function and the health of the lungs and heart.