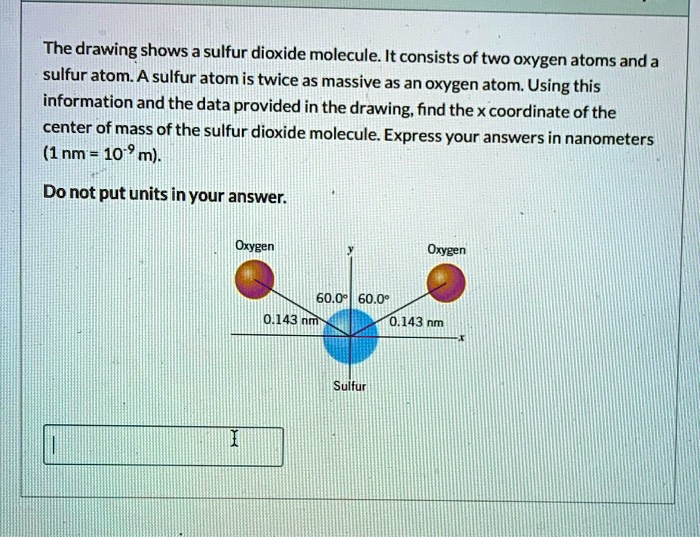
The drawing shows a sulfur dioxide molecule, revealing its intriguing structure and highlighting its significance in various scientific fields. This molecule, composed of one sulfur atom and two oxygen atoms, exhibits unique properties and plays a crucial role in atmospheric chemistry and environmental processes.
Delving into the molecular geometry of sulfur dioxide, we discover its bent shape, resulting from the repulsion between the lone pairs of electrons on the sulfur atom. The bond angles and lengths within the molecule provide insights into its electronic structure and reactivity.
Sulfur Dioxide Molecule Structure
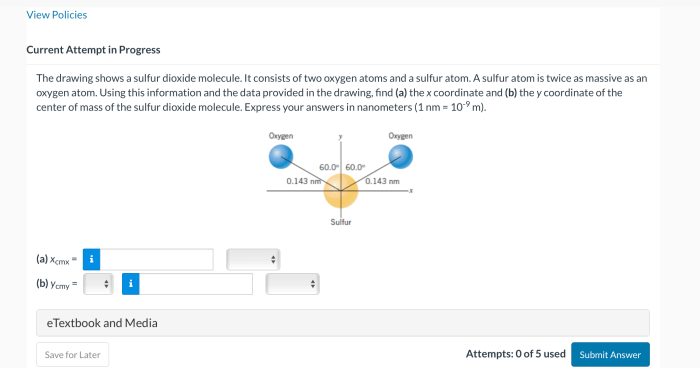
Sulfur dioxide (SO2) is a molecular compound composed of one sulfur atom and two oxygen atoms. The molecular geometry of SO2 is bent or V-shaped, with the sulfur atom at the center and the two oxygen atoms bonded to it.
The bond angles between the sulfur atom and each oxygen atom are approximately 119.5 degrees.
The sulfur-oxygen bond lengths are not equal, with the S-O bond on the side of the molecule being slightly longer than the S-O bond on the top. The S-O bond lengths are approximately 143.1 pm and 149.4 pm, respectively.
Illustration of the Molecule’s Structure
The following illustration shows the structure of a sulfur dioxide molecule:
Properties of Sulfur Dioxide
Physical Properties
- Sulfur dioxide is a colorless gas with a pungent, irritating odor.
- It is denser than air, with a density of 2.926 g/L at 20 °C.
- Its boiling point is -10 °C and its melting point is -72.7 °C.
- Sulfur dioxide is soluble in water, forming sulfurous acid (H2SO3).
Chemical Properties
- Sulfur dioxide is a reactive gas that can undergo a variety of reactions.
- It is a reducing agent and can be oxidized to sulfur trioxide (SO3).
- It can react with water to form sulfurous acid (H2SO3).
- It can also react with bases to form sulfites.
Sources and Applications of Sulfur Dioxide
Natural Sources
- Volcanic eruptions
- Forest fires
- Biological processes, such as the decomposition of organic matter
Anthropogenic Sources
- Industrial processes, such as the combustion of fossil fuels and the smelting of sulfide ores
- Transportation, primarily from the combustion of diesel fuel
- Power plants
Applications
- Bleaching agent for paper and textiles
- Preservative for food and beverages
- Disinfectant
- Fumigant
Environmental Impact of Sulfur Dioxide
Effects on Human Health
- Respiratory irritation
- Eye irritation
- Cardiovascular problems
- Asthma
Effects on the Environment
- Acid rain
- Damage to vegetation
- Corrosion of buildings and monuments
Regulations and Technologies
- Regulations have been implemented to reduce sulfur dioxide emissions, such as the Clean Air Act in the United States.
- Technologies, such as scrubbers and catalytic converters, have been developed to remove sulfur dioxide from industrial and vehicle emissions.
Sulfur Dioxide in the Atmosphere: The Drawing Shows A Sulfur Dioxide Molecule
Role in the Earth’s Atmosphere, The drawing shows a sulfur dioxide molecule
- Sulfur dioxide is a trace gas in the Earth’s atmosphere.
- It is emitted from both natural and anthropogenic sources.
- It can undergo a variety of reactions in the atmosphere, including oxidation to sulfur trioxide and formation of sulfate aerosols.
Interactions with Other Atmospheric Gases and Particles
- Sulfur dioxide can react with other atmospheric gases, such as ozone and hydroxyl radicals.
- It can also react with particulate matter, such as dust and soot.
- These reactions can lead to the formation of sulfate aerosols, which can have a significant impact on climate.
Contribution to Climate Change
- Sulfate aerosols can reflect sunlight back to space, which can have a cooling effect on the Earth’s climate.
- However, sulfate aerosols can also contribute to the formation of clouds, which can have a warming effect.
- The overall impact of sulfur dioxide on climate is complex and is still being studied.
FAQ Overview
What is the molecular geometry of sulfur dioxide?
Sulfur dioxide exhibits a bent molecular geometry due to the repulsion between the lone pairs of electrons on the sulfur atom.
What are the bond angles and lengths in a sulfur dioxide molecule?
The bond angles in sulfur dioxide are approximately 119.5 degrees, and the bond lengths between the sulfur atom and each oxygen atom are approximately 1.43 angstroms.
What are the physical properties of sulfur dioxide?
Sulfur dioxide is a colorless gas with a pungent odor. It is soluble in water and has a boiling point of -10 degrees Celsius.
What are the chemical properties of sulfur dioxide?
Sulfur dioxide is a reactive gas that can undergo a variety of chemical reactions. It is a reducing agent and can react with oxidizing agents to form sulfur trioxide.
What are the sources of sulfur dioxide?
Sulfur dioxide is released into the atmosphere from both natural and anthropogenic sources. Natural sources include volcanic eruptions and the oxidation of organic matter. Anthropogenic sources include the burning of fossil fuels and industrial processes.