Beginning with the graphing periodic trends answer key, this comprehensive guide embarks on an enlightening journey through the fascinating realm of periodic trends. By exploring the intricate relationship between the periodic table and the properties of elements, we unlock a treasure trove of insights into the fundamental building blocks of our universe.
Delving into the steps involved in graphing periodic trends, we unveil the techniques for effectively visualizing these patterns. From selecting the appropriate graph type to interpreting the resulting data, this guide empowers readers with the tools to decipher the periodic table’s hidden messages.
Periodic Trends
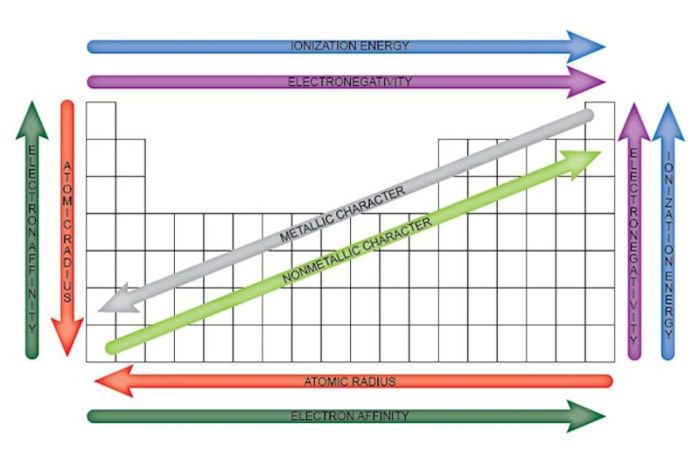
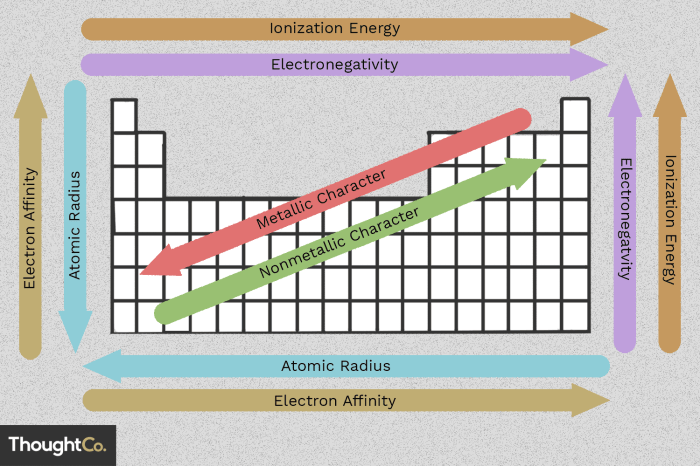
Periodic trends are the predictable changes in the properties of elements as you move across a period (row) or down a group (column) of the periodic table. These trends are a result of the regular increase in atomic number, which determines the number of protons and electrons in an atom.
Some of the most important periodic trends include:
- Atomic radius: The atomic radius is the distance from the nucleus to the outermost electron shell. It generally decreases across a period and increases down a group.
- Ionization energy: The ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom. It generally increases across a period and decreases down a group.
- Electronegativity: The electronegativity is the ability of an atom to attract electrons. It generally increases across a period and decreases down a group.
Graphing Periodic Trends, Graphing periodic trends answer key
Graphing periodic trends is a useful way to visualize the changes in properties across the periodic table. The following steps can be used to graph periodic trends:
- Choose the appropriate type of graph. The most common types of graphs used to graph periodic trends are line graphs and bar graphs.
- Plot the data on the graph. The independent variable (the property being graphed) is plotted on the y-axis, and the dependent variable (the position of the element on the periodic table) is plotted on the x-axis.
- Draw a line or curve to connect the data points. The line or curve should show the general trend of the data.
Analyzing Periodic Trends
Analyzing periodic trends can help you to understand the relationships between the properties of elements and their position on the periodic table. The following are some of the ways to analyze periodic trends:
- Identify patterns and trends in the data. Look for any regular changes in the data as you move across a period or down a group.
- Use the trends to predict the properties of other elements. Once you have identified the trends, you can use them to predict the properties of other elements that are in the same group or period.
Applications of Periodic Trends
Periodic trends are used in a variety of fields of science, including chemistry, physics, and biology. Some of the applications of periodic trends include:
- Designing new materials. Periodic trends can be used to design new materials with specific properties.
- Predicting chemical reactions. Periodic trends can be used to predict the products of chemical reactions.
- Understanding biological processes. Periodic trends can be used to understand the role of elements in biological processes.
Clarifying Questions: Graphing Periodic Trends Answer Key
What are periodic trends?
Periodic trends refer to the systematic variations in the properties of elements as we move across the periodic table from left to right and top to bottom.
How do I graph periodic trends?
Graphing periodic trends involves plotting the values of a particular property against the atomic number of the elements. The resulting graph reveals the periodic variations in that property.
What are some examples of periodic trends?
Common periodic trends include atomic radius, ionization energy, electronegativity, and metallic character.