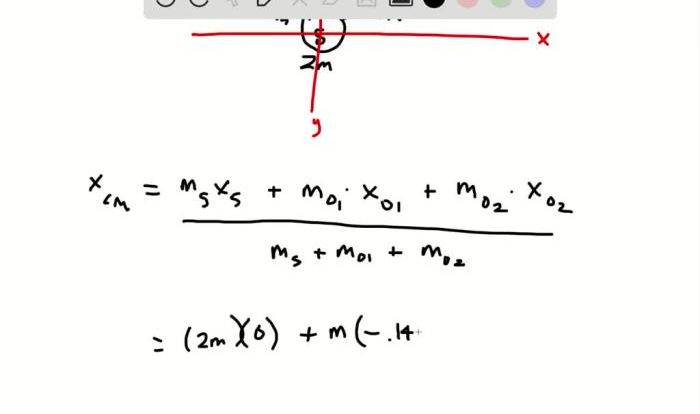
Unit Chemical Reactions Predicting Products – DR/C – WS #6 introduces the fundamental principles of predicting products in chemical reactions, elaborates on the methods for balancing chemical equations, and categorizes different types of chemical reactions based on their characteristics. The Artikel also discusses the factors that influence the rate and direction of chemical reactions and provides examples of practical applications of chemical reactions in various fields.
Predicting Chemical Reaction Products: Unit Chemical Reactions Predicting Products – Dr/c – Ws #6
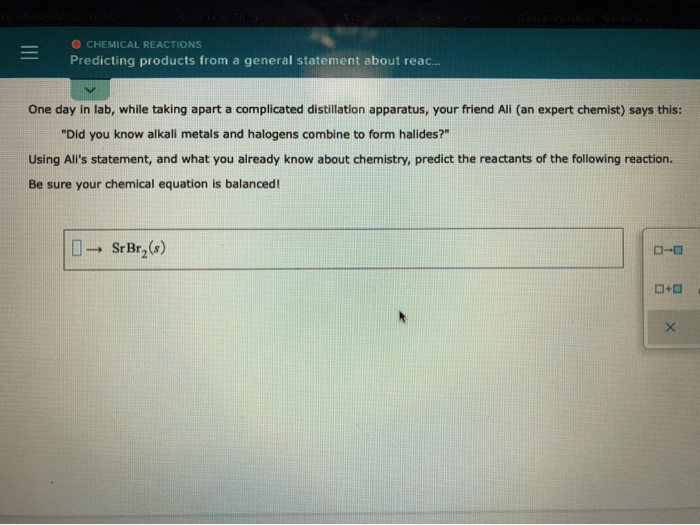
Predicting the products of a chemical reaction is a fundamental skill in chemistry. By understanding the principles of chemical reactivity and the rules governing chemical equations, we can accurately determine the outcome of a given reaction.
The key to predicting products lies in understanding the concept of stoichiometry, which deals with the quantitative relationships between reactants and products. Balanced chemical equations provide a roadmap for predicting products by showing the exact proportions of reactants and products involved in a reaction.
Balancing Chemical Equations
Balancing chemical equations ensures that the number of atoms of each element is the same on both sides of the equation. This is achieved by adjusting the coefficients in front of each chemical formula. The coefficients represent the relative amounts of reactants and products involved in the reaction.
To balance an equation, follow these steps:
- Identify the unbalanced equation.
- Start by balancing the most complex molecule.
- Balance each element one at a time, beginning with the element that appears in the most compounds.
- Check the balance of all elements and make adjustments as needed.
Types of Chemical Reactions
Chemical reactions can be classified into different types based on their characteristics. Some common types include:
- Synthesis reactions: Two or more substances combine to form a single product.
- Decomposition reactions: A single substance breaks down into two or more products.
- Single displacement reactions: One element replaces another in a compound.
- Double displacement reactions: Two compounds exchange ions to form two new compounds.
- Combustion reactions: A substance reacts with oxygen to produce heat and light.
Factors Influencing Chemical Reactions
The rate and direction of chemical reactions are influenced by several factors, including:
- Concentration: Higher concentrations of reactants lead to faster reaction rates.
- Temperature: Higher temperatures increase the kinetic energy of reactants, leading to more frequent and effective collisions.
- Surface area: Increased surface area provides more contact between reactants, enhancing reaction rates.
- Catalysts: Catalysts are substances that speed up reactions without being consumed.
- Equilibrium constants: Equilibrium constants indicate the extent to which a reaction will proceed in a given direction.
Applications of Chemical Reactions, Unit chemical reactions predicting products – dr/c – ws #6
Chemical reactions play a vital role in numerous fields, including:
- Energy production: Fossil fuels undergo combustion reactions to generate electricity.
- Materials synthesis: Chemical reactions are used to create new materials with specific properties.
- Environmental remediation: Chemical reactions can be used to remove pollutants from the environment.
Common Queries
What are the fundamental principles of predicting products in chemical reactions?
The fundamental principles of predicting products in chemical reactions involve understanding the conservation of mass, the law of definite proportions, and the concept of chemical equilibrium.
How are chemical equations balanced?
Chemical equations are balanced by adjusting the coefficients in front of each reactant and product to ensure that the number of atoms of each element is the same on both sides of the equation.
What are the different types of chemical reactions?
Chemical reactions can be classified into various types based on their characteristics, such as synthesis, decomposition, single displacement, double displacement, and combustion reactions.
What factors influence the rate and direction of chemical reactions?
The rate and direction of chemical reactions are influenced by factors such as concentration, temperature, surface area, and the presence of catalysts.
What are some practical applications of chemical reactions?
Chemical reactions have numerous practical applications in fields such as energy production, materials synthesis, environmental remediation, and medicine.