The federal in federalism worksheet – The “Federal in Federalism Worksheet” embarks on an intellectual journey that delves into the intricacies of federalism, its principles, and its implications. This comprehensive guide unravels the distribution of power, the roles of federal and state governments, and the dynamics of their interplay.
Federalism, a complex system of governance, has shaped nations worldwide. Understanding its nuances is paramount for comprehending the delicate balance between unity and diversity, centralization and decentralization.
1. Understanding the Concept of Federalism
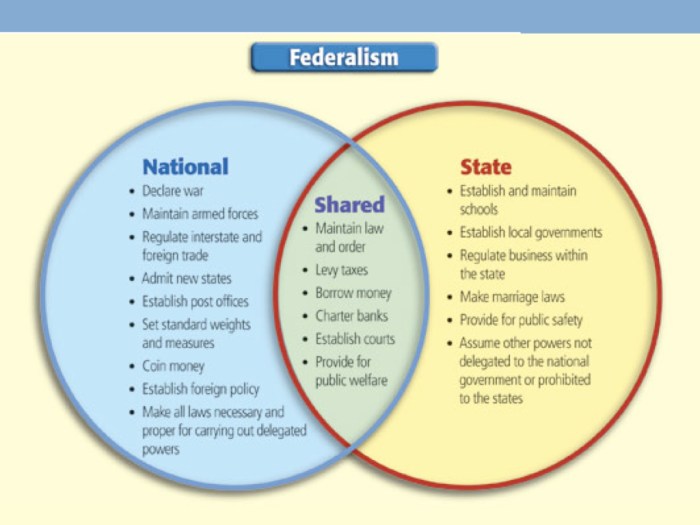
Federalism is a system of government in which power is divided between a central government and several regional governments. This distribution of power allows for both centralized decision-making and local autonomy.
Federal systems typically exhibit the following characteristics:
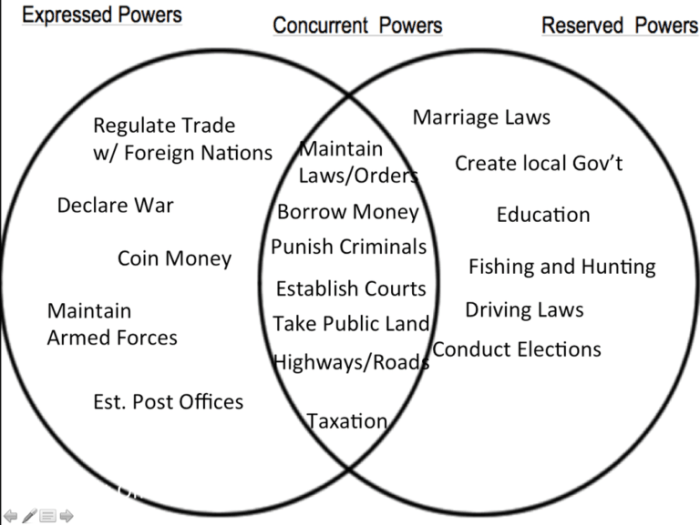
- A written constitution that defines the powers of the federal and state governments
- A division of powers between the federal and state governments, with each level having exclusive and concurrent powers
- A supreme court or other judicial body that interprets the constitution and resolves disputes between the federal and state governments
Examples of federal systems include the United States, Canada, Australia, and Germany.
2. The Federal Government’s Role
The federal government in a federal system typically has the following powers and responsibilities:
- Foreign policy and national defense
- Interstate and international commerce
- Currency and monetary policy
- Taxation
- Regulation of interstate transportation and communication
The federal government is usually organized into three branches:
- Legislative branch (e.g., Congress in the US)
- Executive branch (e.g., the President in the US)
- Judicial branch (e.g., the Supreme Court in the US)
3. The State Governments’ Role
State governments in a federal system typically have the following powers and responsibilities:
- Education
- Public health and safety
- Regulation of intrastate commerce
- Taxation
- Land use planning
State governments are usually organized into three branches:
- Legislative branch (e.g., state legislature)
- Executive branch (e.g., governor)
- Judicial branch (e.g., state supreme court)
4. The Relationship Between Federal and State Governments: The Federal In Federalism Worksheet
The relationship between the federal and state governments in a federal system is characterized by both cooperation and tension.
The two levels of government cooperate in areas such as:
- Infrastructure development
- Disaster relief
- Law enforcement
However, the two levels of government may also come into conflict over issues such as:
- Taxation
- Regulation
- Environmental protection
5. Challenges and Opportunities in Federalism
Federalism presents both challenges and opportunities for governments.
Challenges include:
- Balancing the powers of the federal and state governments
- Coordinating policies between the two levels of government
- Addressing regional disparities
Opportunities include:
- Providing for both centralized decision-making and local autonomy
- Allowing for experimentation and innovation at the state level
- Promoting national unity while preserving regional diversity
Q&A
What is the primary objective of federalism?
Federalism aims to balance the need for a strong central authority with the preservation of regional autonomy, fostering both unity and diversity.
How are powers typically distributed in a federal system?
Federal systems generally divide powers between the central government and regional or state governments, with each level exercising authority over specific areas.
What are some common challenges faced by federal systems?
Federal systems often grapple with issues such as power imbalances, regional disparities, and the need for effective coordination between different levels of government.
